The master boot record (MBR) is a boot sector on a storage device that contains information about how the device is partitioned.
The MBR also contains instructions for locating the operating system (OS). The computer accesses the MBR, then follows the program to load operating system data into random access memory (RAM). That allows your operating system to boot up.
The MBR is about 512 bytes. It’s also known as the master partition table, and it’s similar (but not identical) to a GUID Partition Table (GPT). GPT is a newer architecture that enables larger partition sizes and is less prone to corruption; most modern hard drives use GPT instead of MBR.
What happens if the MBR becomes corrupted?
If the boot record is corrupt, the operating system won’t load. However, the hard drive’s data is usually recoverable, since the MBR constitutes a very small portion of the drive.
Windows computers can often resolve MBR corruption automatically, though the user may need to insert an external recovery device (such as a flash drive or an optical disc) to allow the operating system to boot for the repair.
But if data corruption occurs due to a hardware failure — such as a head crash — the hard drive will need to be treated in a professional data recovery laboratory. Engineers will need to address the physical issues in a certified cleanroom, then make a complete copy (clone) of all of the data.
Is GPT more reliable than MBR?
Yes, though no disk architecture technology is perfect — GUID partition tables can be lost, though this is rare outside of hardware failures or user error.
GPT is an improvement on MBR for several reasons:
- GPT allows for larger partitions. As hard drive areal density has increased, larger partitions have become more essential for modern computing.
- The GPT scheme also has more consistent rules than MBR, which limits the potential for certain problems. For example, MBR drives may use “hidden” sectors to store information, and poor implementations can lead to severe symptom problems.
- GPT drives also include a protective MBR, which enables legacy applications to utilize the storage device (even if they don’t support the GPT disk structure).
How can I determine whether my hard drive uses MBR or GPT?
In Windows 7 or later, follow these steps:
- Press the Windows Key + X. This opens a menu with system tools.
- Select Disk Management.
- Find the hard drive you’d like to inspect at the bottom of the screen (not in the top panel, which shows partition info). Right-click and select Properties.
- Switch to the Volumes tab. Look for “Partition Style.”
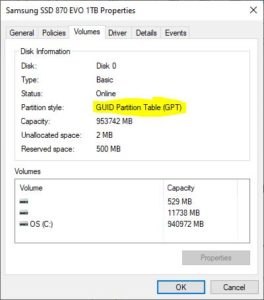
A view of the disk architecture information in Windows’ Disk Management tool, with GPT highlighted.
What error messages indicate an issue with the Master Boot Record?
If the MBR isn’t functioning as expected, your operating system won’t boot. You might also encounter one of these error identifiers:
- MBR Error 1
- MBR Error 2
- MBR Error 3
Data corruption is the most common cause of these errors, but if you’ve recently changed something about your hardware, that could also cause a boot failure (for example, if you’ve installed a new secondary hard drive and your computer is attempting to boot from the wrong device).
Because MBR issues can indicate hardware failure, we strongly recommend working with a professional data recovery provider before attempting to repair the Master Boot Record. That’s especially important if you’ve noticed other symptoms such as clicking sounds, slow operation, or other incidences of corruption.
However, if you’ve backed up your data, you can attempt to repair the MBR by using a recovery disk. Here’s Microsoft’s guide for creating and using a recovery drive, which also includes info about other recovery options.
Trust your data to the world leader in professional data recovery.
Datarecovery.com operates full-service laboratories at every location. Each is equipped with certified cleanrooms, dedicated firmware repair tools, and other technologies needed to safely recover data from hard drives, solid-state drives, and other storage devices.
We support our services with a no data, no charge guarantee: If we’re unable to recover the files you need, you don’t pay for the attempt. With risk-free evaluations and fast turnaround times, we provide the peace of mind you need to recover from any data disaster.
Get started by scheduling a free evaluation online or call 1-800-237-4200 to connect with an expert.





