If your computer has been infected with TorrentLocker ransomware, Datarecovery.com offers expert services to eliminate the malware from your computer and restore encrypted files. This page contains detailed information on TorrentLocker and its variants. However, it’s important to note that no two cases are precisely the same, and new TorrentLocker variants may not share the attributes of the malware described in this article.
To get started or to discuss options for your computer, call us today at 1-800-237-4200 and ask to speak to a ransomware recovery specialist.
What is TorrentLocker (And How Does It Work)?
TorrentLocker ransomware appeared in September of 2013 and began spreading in February of 2014, and it’s still a major threat for computer users. It is often incorrectly described as a CryptoLocker variant. It is unrelated to CryptoLocker, but it does use the CryptoLocker name in an apparent attempt to take advantage of CryptoLocker’s notoriety.
When TorrentLocker executes, it searches for certain file types on a computer’s local and network storage media, then encrypts those files. It communicates with a Command and Control (C&C) server, which generates a unique user key. The victim is presented with a message that indicates that his or her files are encrypted, at which point the victim is asked to pay a ransom via bitcoin, an untraceable cryptocurrency.
Notable Features of TorrentLocker Ransomware Include:
- Unlike most other ransomware programs, TorrentLocker is geographically targeted. This means that it targets victims based on their geographic locations, using official-looking emails from the targeted country (or state) to trick the victim into opening infected files.
- The victim’s files are encrypted with a symmetric block cipher AES (Advanced Encryption System). The AES key is encrypted with an asymmetric cipher RSA cryptosystem.
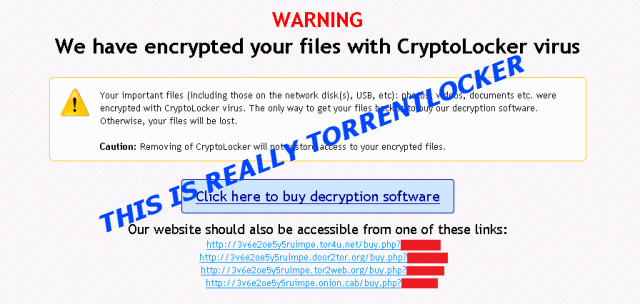
- TorrentLocker’s name comes from a registry key that it creates when it infects a host machine. However, the program does not refer to itself as “TorrentLocker.” Instead, it claims to be CryptoLocker, a well-known ransomware program. TorrentLocker is fundamentally different from CryptoLocker, however. This causes significant confusion among victims and ransomware experts. A sample encryption warning message is below.
- TorrentLocker allows users to decrypt one file “for free.” This is a common feature among ransomware programs. The goal is to prove to the victim that their files can be decrypted. If the victim pays the ransom, TorrentLocker provides a tool that can be used to decrypt all affected files associated with the user’s unique ID.
A list of file formats targeted by TorrentLocker appears below.
*.3ds, *.3fr, *.3pr, *.7z, *.ab4, *.ac2, *.accdb, *.accde, *.accdr, *.accdt, *.acr, *.adb, *.agd1, *.ai, *.ait, *.al, *.apj, *.arw, *.asm, *.asp, *.awg, *.backup, *.backupdb, *.bak, *.bdb, *.bgt, *.bik, *.bkp, *.blend, *.bpw, *.c, *.cdf, *.cdr, *.cdr3, *.cdr4, *.cdr5, *.cdr6, *.cdrw, *.cdx, *.ce1, *.ce2, *.cer, *.cfp, *.cgm, *.cib, *.cls, *.cmt, *.cpi, *.cpp, *.cr2, *.craw, *.crt, *.crw, *.csh, *.csl, *.css, *.csv, *.dac, *.db, *.db-journal, *.db3, *.dbf, *.dc2, *.dcr, *.dcs, *.ddd, *.ddoc, *.ddrw, *.der, *.design, *.dgc, *.djvu, *.dng, *.doc, *.docm, *.docx, *.dot, *.dotm, *.dotx, *.drf, *.drw, *.dwg, *.dxb, *.erbsql, *.erf, *.exf, *.fdb, *.ffd, *.fff, *.fh, *.fhd, *.fpx, *.fxg, *.gray, *.grey, *.gry, *.h, *.hbk, *.hpp, *.ibank, *.ibd, *.ibz, *.idx, *.iiq, *.incpas, *.jpeg, *.jpg, *.js, *.kc2, *.kdbx, *.kdc, *.kpdx, *.lua, *.mdb, *.mdc, *.mef, *.mfw, *.mmw, *.moneywell, *.mos, *.mpg, *.mrw, *.myd, *.ndd, *.nef, *.nop, *.nrw, *.ns2, *.ns3, *.ns4, *.nsd, *.nsf, *.nsg, *.nsh, *.nwb, *.nx1, *.nx2, *.nyf, *.odb, *.odf, *.odg, *.odm, *.odp, *.ods, *.odt, *.orf, *.otg, *.oth, *.otp, *.ots, *.ott, *.p12, *.p7b, *.p7c, *.pat, *.pcd, *.pdf, *.pef, *.pem, *.pfx, *.php, *.pl, *.pot, *.potm, *.potx, *.ppam, *.pps, *.ppsm, *.ppsx, *.ppt, *.pptm, *.pptx, *.ps, *.psafe3, *.psd, *.ptx, *.py, *.ra2, *.raf, *.rar, *.raw, *.rdb, *.rtf, *.rw2, *.rwl, *.rwz, *.s3db, *.sas7bdat, *.sav, *.sd0, *.sd1, *.sda, *.sdf, *.sldm, *.sldx, *.sql, *.sqlite, *.sqlite3, *.sqlitedb, *.sr2, *.srf, *.srw, *.st4, *.st5, *.st6, *.st7, *.st8, *.stc, *.std, *.sti, *.stw, *.stx, *.sxc, *.sxd, *.sxg, *.sxi, *.sxm, *.sxw, *.txt, *.wb2, *.x3f, *.xla, *.xlam, *.xll, *.xlm, *.xls, *.xlsb, *.xlsm, *.xlsx, *.xlt, *.xltm, *.xltx, *.xlw, *.xml, *.ycbcra, *.zip
This may not be a complete list, as new variants may add or remove certain formats.
How Does TorrentLocker Infect My System?
The vast majority of new TorrentLocker infections occur when a victim opens a spam email. These emails usually appear to come from official sources. Some have executable files attached to them (these may appear to be PDF files), while others have Microsoft Word documents that ask to have macros enabled. If the macro is enabled, the computer will download an executable from a TorrentLocker server.
The best way to avoid a TorrentLocker infection is to avoid emails from unknown sources. Never open attachments if you’re at all unsure about them, and don’t trust your antivirus software to catch all ransomware variants. Businesses can also prevent TorrentLocker infections by using firewalls that block Tor and I2P servers.

What Ransom Payment Does Torrent Locker Demand for Decrypting Files?
TorrentLocker asks for a ransom of up to 4.081 bitcoin (about $1900 when this article was written) for decryption. However, the exact amount is localized based on the currency of the victim’s home country.
Can I Disable TorrentLocker Encryption?
Early versions of TorrentLocker could be easily decrypted due to a flaw in the program’s design. However, no decryption cracks exist for newer variants.
Datarecovery.com can help you create a ransomware recovery plan for TorrentLocker or CryptoLocker infection. Our experts have experience with every type of ransomware, and we offer services for both businesses and personal computer users. As a last resort, we can organize a secure payment of the ransom to restore your files, but our primary objective is always to resolve the infection without rewarding ransomware creators. For more information, speak with a ransomware decryption expert by calling 1-800-237-4200.




